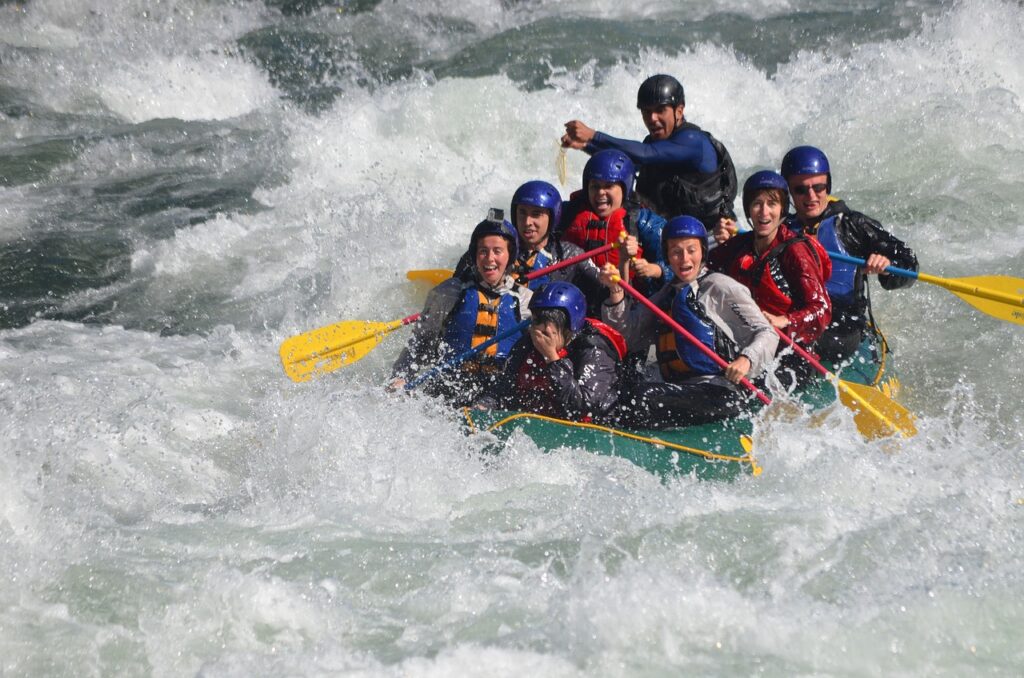
The Shift Toward Experiences: A Cultural Evolution
Generation Z, born between the mid-1990s and early 2010s, is spearheading a significant shift in consumer behavior. This cohort is increasingly prioritizing experiences over material possessions, a trend that reflects their unique values, aspirations, and the cultural landscape they’ve grown up in.
The Quest for Personal Fulfillment
For Gen Z, the pursuit of personal growth and self-discovery is paramount. They view experiences as gateways to self-improvement and meaningful engagement with the world around them. Unlike physical possessions, experiences offer opportunities for learning, skill development, and personal transformation.
Examples of experiences that align with Gen Z’s desire for personal fulfillment:
- Immersive travel experiences: Backpacking trips, cultural exchanges, volunteer tourism
- Skill-building workshops: Coding bootcamps, art classes, culinary courses
- Wellness retreats: Yoga retreats, meditation seminars, fitness challenges
- Music festivals and concerts: Multi-day events combining music, art, and culture
- Adventure sports: Skydiving, rock climbing, surfing lessons
- Cultural events: Art exhibitions, film festivals, theater performances
- Sustainability workshops: Eco-living seminars, zero-waste challenges
- Digital nomad experiences: Remote work programs in different locations
- Social impact initiatives: Community service projects, charity events
- Tech-based experiences: Virtual reality experiences, augmented reality art shows
These experiences offer Gen Z the opportunity to express their individuality, challenge themselves, and connect with like-minded individuals. They value the personal growth and stories that come from these experiences far more than the temporary satisfaction of acquiring material goods.
Emotional Connection and Lasting Memories
Experiences create emotional bonds and long-lasting memories that material items often fail to provide. This emotional resonance is a key factor in Gen Z’s preference for experiential consumption.
| Aspect | Experiential Purchases | Material Goods |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Retention | High – creates vivid, lasting memories | Low – novelty often wears off quickly |
| Emotional Impact | Strong – often associated with positive emotions | Variable – initial excitement may fade |
| Social Connection | High – often shared with others | Limited – typically individual consumption |
| Personal Growth | Significant – opportunities for learning and development | Minimal – unless tied to a skill or hobby |
| Adaptability | Flexible – can be tailored to personal preferences | Fixed – limited by product features |
| Storytelling Value | High – provides material for personal narratives | Low – unless the item has unique significance |
| Anticipation Factor | Extended – enjoyment before, during, and after | Short-lived – primarily before acquisition |
The emotional impact of experiences extends beyond the moment of consumption. Gen Z values the anticipation before an experience, the immersion during it, and the reflection afterward. This three-stage enjoyment process contributes to a more sustained sense of satisfaction compared to the often fleeting pleasure of acquiring material goods.
Economic Factors Influencing Gen Z’s Preferences

The economic landscape faced by Gen Z has significantly shaped their consumption patterns and preferences. Growing up in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis and facing unique economic challenges has led this generation to adopt a more pragmatic and value-driven approach to spending.
Financial Challenges and Minimalism
Gen Z is navigating a complex economic environment characterized by rising living costs, student debt, and income uncertainty. These factors have fostered a sense of financial pragmatism and a lean towards minimalism in material possessions.
Strategies Gen Z uses to balance finances while enjoying experiences:
- Budget prioritization: Allocating funds specifically for experiences
- Subscription-based experiences: Utilizing services like ClassPass for varied activities
- Group experiences: Sharing costs with friends for travel or events
- Off-peak timing: Choosing less expensive times for travel or activities
- Local exploration: Finding unique experiences in their own cities or regions
- Skill-sharing: Exchanging skills or services for experiences
- Loyalty programs: Maximizing points and rewards for experiential purchases
- Side hustles: Taking on additional work to fund experiential spending
- DIY experiences: Creating their own events or workshops
- Virtual experiences: Engaging in online classes or virtual tours
This approach allows Gen Z to maximize their experiential consumption while minimizing financial strain. They’re more likely to invest in a memorable concert or a skill-building workshop than in the latest gadget or fashion item.
Value-Driven Consumerism
Gen Z exhibits a heightened consciousness about where and how they spend their money. They gravitate towards businesses and experiences that align with their values, particularly those focused on sustainability, social responsibility, and ethical practices.
| Brand | Type of Experience | Sustainability/Social Impact Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Airbnb | Travel accommodations | Community-based tourism, local economic impact |
| Patagonia | Outdoor adventures | Environmental conservation, sustainable materials |
| The Body Shop | Beauty workshops | Ethical sourcing, animal welfare, community trade |
| TOMS | Travel and voluntourism | One-for-one giving model, social entrepreneurship |
| Ecosia | Tech-based (search engine) | Tree planting, carbon-neutral operations |
| Lush | DIY cosmetics workshops | Packaging-free products, ethical sourcing |
| REI | Outdoor education classes | Sustainability initiatives, cooperative business model |
| WeWork | Coworking experiences | Community building, urban revitalization |
| Impossible Foods | Plant-based food experiences | Reducing environmental impact of meat consumption |
| Warby Parker | Eyewear try-on experiences | Buy-a-pair, give-a-pair program |
These brands exemplify the kind of experiential offerings that resonate with Gen Z’s values. By choosing to support such businesses, Gen Z consumers feel they are not just purchasing an experience, but also contributing to broader social and environmental causes.
The Role of Social Media and Digital Influence
Social media platforms play a pivotal role in shaping Gen Z’s preference for experiences over material goods. These digital spaces serve as both inspiration for experiential consumption and platforms for sharing and validating these experiences.
Instagram-Worthy Moments
The visual nature of platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat has created a culture where shareable, aesthetic experiences are highly valued. Gen Z seeks out experiences that not only provide personal fulfillment but also offer opportunities for creative expression and social engagement through digital sharing.
Popular experiences that trend on social media:
- Music festivals: Coachella, Glastonbury, Tomorrowland
- Street art tours: Exploring urban murals and graffiti
- Pop-up museums: Color Factory, Museum of Ice Cream
- Themed cafes and restaurants: Cat cafes, dining in the dark experiences
- Extreme sports: Bungee jumping, wingsuit flying
- Unique accommodations: Treehouses, ice hotels, underwater rooms
- Food challenges: Trying exotic cuisines or oversized dishes
- Light festivals: Vivid Sydney, Amsterdam Light Festival
- Immersive art installations: Teamlab Borderless, Meow Wolf
- Wellness retreats: Silent retreats, forest bathing experiences
These experiences are chosen not just for personal enjoyment, but also for their photogenic qualities and potential to generate engaging content. The act of sharing these experiences on social media becomes an integral part of the consumption process, extending the enjoyment beyond the actual event.
Influence of Digital Communities
Digital communities and influencers wield significant influence over Gen Z’s experiential preferences. These online spaces serve as trusted sources of recommendations and validation for various experiences.
The impact of digital communities on Gen Z’s experiential choices:
- Authenticity and relatability: Gen Z values recommendations from peers and relatable influencers over traditional advertising.
- Niche experiences: Online communities help uncover unique, off-the-beaten-path experiences that align with specific interests.
- Real-time feedback: Social media provides instant reviews and feedback on experiences, helping Gen Z make informed decisions.
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): Seeing peers share experiences online can drive desire to participate in similar activities.
- Collective experience planning: Digital platforms facilitate group planning for shared experiences.
- Virtual experiences: Online communities introduce Gen Z to digital-only experiences, like virtual concerts or online gaming events.
- Skill-sharing communities: Platforms like YouTube and TikTok inspire DIY experiences and skill acquisition.
- Cultural exchange: Global online communities expose Gen Z to diverse cultural experiences they might seek out.
- Cause-driven experiences: Social media amplifies experiences tied to social or environmental causes.
- Trend forecasting: Digital influencers often predict and shape upcoming experiential trends.
These digital ecosystems not only inspire Gen Z’s experiential choices but also provide platforms for them to become content creators and influencers themselves, further reinforcing the cycle of experiential consumption and sharing.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations

Gen Z’s preference for experiences over material goods is deeply intertwined with their strong commitment to sustainability and ethical consumption. This generation is acutely aware of the environmental and social impacts of their purchasing decisions.
Experiences Over Materialism for Environmental Impact
The environmental consciousness of Gen Z leads them to favor experiences that have a lower ecological footprint compared to the production and consumption of material goods.
| Aspect | Material Goods | Experiential Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Use | High – requires raw materials, manufacturing | Lower – often utilizes existing infrastructure |
| Waste Generation | Significant – packaging, obsolescence | Minimal – typically produces less physical waste |
| Carbon Footprint | Often high due to production and shipping | Variable – can be low, especially for local experiences |
| Longevity | Limited – often replaced or discarded | Lasting – memories and skills endure |
| Reusability | Limited – often single-owner use | High – same experience can be enjoyed by many |
| Environmental Education | Limited – unless explicitly eco-focused products | High – many experiences involve nature or sustainability education |
| Biodiversity Impact | Can be significant due to resource extraction | Often minimal, some experiences actively support conservation |
| Energy Consumption | Ongoing – many products require constant energy | Time-limited – energy use often confined to the duration of the experience |
This comparison illustrates why Gen Z often views experiential consumption as a more environmentally responsible choice. Experiences like eco-tourism, nature retreats, or sustainability workshops not only have a lower environmental impact but also often contribute to environmental education and conservation efforts.
Ethical Spending: Aligning Purchases with Values
Gen Z strongly believes in using their purchasing power to support causes and businesses that align with their ethical values. They seek out experiences that not only provide personal enjoyment but also contribute positively to society and the environment.
Top ethical experience-based companies supported by Gen Z:
- Intrepid Travel: Offers sustainable, small-group adventure tours with a focus on local communities and environmental conservation.
- Kiva: Provides experiences in microfinance and social entrepreneurship through peer-to-peer lending.
- WWOOF (World Wide Opportunities on Organic Farms): Connects volunteers with organic farms, promoting sustainable agriculture and cultural exchange.
- The Ethical Experience Company: Curates ethical travel experiences that support local communities and conservation efforts.
- Fairbnb: A cooperative alternative to traditional vacation rentals, ensuring profits benefit local communities.
- OneSeed Expeditions: Adventure travel company that invests in local entrepreneurs in the destinations they visit.
- Unseen Tours: Offers city tours led by homeless and formerly homeless guides, providing employment opportunities.
- Conscious Festivals: Music and arts festivals with a strong focus on sustainability and social impact, like Lightning in a Bottle or Envision Festival.
- Impact Travel Alliance: A global community and nonprofit promoting sustainable tourism experiences.
- G Adventures: Adventure travel company partnering with National Geographic to offer educational and sustainable tours.
These companies exemplify how experiences can be designed to create positive social and environmental impact. By choosing such experiences, Gen Z feels they are not just consumers, but active participants in creating a more sustainable and equitable world.
The preference for ethical experiences extends beyond travel and tourism. Gen Z also values local experiences that contribute to community development, educational experiences that promote social justice, and creative experiences that support artists and cultural preservation.
This alignment of experiences with personal values allows Gen Z to feel good about their spending while also gaining memorable experiences. It reflects a holistic approach to consumption where the impact of their choices on society and the environment is as important as the personal enjoyment derived from the experience.
In conclusion, Gen Z’s preference for experiences over material goods is a multifaceted trend driven by their quest for personal growth, desire for meaningful connections, economic pragmatism, digital native status, and strong ethical and environmental values. This shift represents not just a change in consumption patterns, but a broader redefinition of what constitutes value and fulfillment for a new generation. As Gen Z’s influence in the market grows, businesses and brands will need to adapt, offering more experiential, sustainable, and socially responsible options to meet the evolving demands of this values-driven cohort.